Homa Bay, Kenya MARCH 4, 2020 — With more than half of the estimated 2.2 billion people to be added to the global population by 2050 expected to be from the African continent, according to the UN report on global population, this rapid growth and its development policies, especially in Sub-Saharan Africa will inhibit efforts to alleviate poverty, ensuring food security, preserving the environment, and improving Africans’ well-being, increasing vulnerability to climate change impacts and undermine sustainable development efforts on the continent.
Staring at a crisis in which some 256 million people are facing hunger, and where much of its current discourse on food security is focused on increasing and expanding agricultural production, the African continent’s expansion in agricultural production is speculated to be at the expense of natural resources.
As one of the solutions, an ambitious program dubbed Regreening Africa, a multi-country project funded by the European Union is seeking to scale up evergreen agriculture targeting an estimated 500,000 farm households over an area of one million hectares by 2022.
The eight beneficiary countries; Kenya, Somalia, Ethiopia, and Rwanda in East Africa and West Africa’s Niger, Mali, Ghana, and Senegal are at the forefront in restoring already degraded land to more productive use.
The project builds on the considerable experience in land restoration consortium partners which are World Agroforestry Centre as project lead, World Vision, Catholic Relief Services (CRS), CARE, Oxfam, and Sahel Eco.
“We are blending research with development and identify practices that are suitable for the different kinds of farms that we are working across the eight countries in East Africa and West Africa’s Sahel region. Working with research and development partners together helps us to be able to make decisions that are informed by scientific evidence,” Susan Chomba, Regreening Africa Project Manager told Ubuntu Times in an interview.
The project encourages the use of Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR), a quick, affordable and easy-to-replicate way of restoring and improving agricultural, forested and pasture lands by promoting systematic regrowth of existing trees or from naturally occurring tree seeds. It can be used wherever there are living tree stumps with the ability to coppice (re-sprout) or seeds in the soil that will germinate.

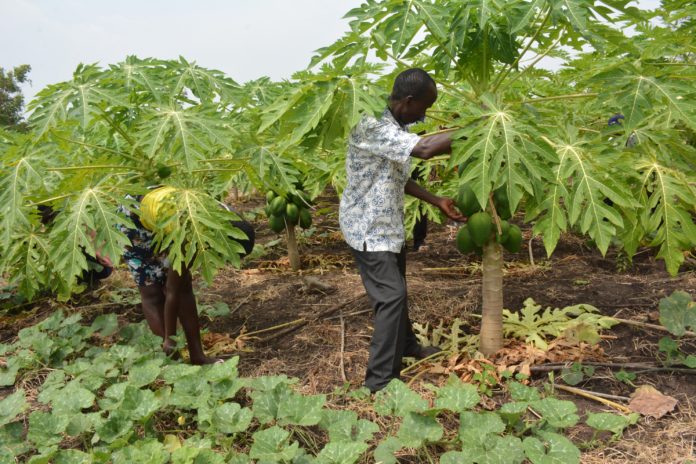
Maxwell Ochoo, 32-year old father of four, quit his job as a community health mobilizer to engage in farming, a risky venture amidst degraded land in Lambwe, Kenya’s lakeside region.
“I worked as a community health mobilizer but when my contract ended, I resorted to try [my] luck in farming. It was a challenging undertaking with degraded land where none believed it would one day turn green,” says Ochoo.
After successfully practicing FMNR on his farm, Ochoo is currently a proud farmer as he is able to take his children to school, thanks to reliable income from his pawpaw fruits and a fish pond he established on his farm.

To minimize food cost for fish, I utilize calliandra — a small tropical legume tree he planted on his land, whose dry leaves are consumed by fish.
Farmers increase food security by retaining trees on agricultural land, by encouraging natural regeneration and by planting trees and other forest plants. For most of the year, herders in arid and semi-arid lands depend on trees as a source of fodder for their livestock.
Nancy Kemboi, a smallholder farmer in Baringo, a region characterized by constant drought also benefited on this simple innovative technique of protecting wildlings and pruning stumps that coppice so they rapidly regrow into trees.
Together with her husband, Nancy, through a capacity building on the FMNR skills offered by World Vision Kenya, she started regenerating indigenous trees such as acacia and re-growing pasture in the same field to cushion her livestock during extreme drought periods.
Africa’s indigenous trees coppice when cut, their stumps looking like weeds, but when farmers select the tallest and straight stems and cull the rest, trees rapidly grow.

“At first, the practice seemed [like] it would take long, but with patience and continuous pruning of the trees, benefits started to trickle. My children could not spend time having to fetch fuel wood mile away. I started getting fuel from tree branches, a product of pruning of growing sprouts,” Nancy told an interview at her farm.
Nancy’s children field soon started to contrast with the bare bleak ones of her neighbors. Her livestock started to thrive, with milk production increasing due to the availability of quality pasture.
“Before practicing FMNR, I used to get merely five-liter of milk a day from my cows, selling it to middlemen who used to buy at low prices,” says Nancy, adding that since her milk production increased, she now sells her milk to a nearby dairy facility.

Lilian Dodzo, World Vision Kenya Country Director says the decision to train and capacity-build farmers with simple skills on how to mitigate against the changing climate is such a big phenomenon in the current environment.
“It is important to build skills in our communities to find very simple and low-cost ways in which we can mitigate against climate change to be able to build the resilience of our communities,” Dodzo told in an interview.
She adds, “Our greatest interest in these activities is to see what it contributes to the child well-being. With access to pasture and more milk to sell, the income goes all the way to helping pay for children school fees, buy food and develop gardens where women can grow drought-resistant crops.”
According to Clare Rogers, World Vision Australia Chief Executive Officer, Nancy’s courageous move has not only changed her family but the community and farms around her area, with her neighbors starting to adopt the same approach after losing livestock to drought being an inspiration for the future.
“Nancy and her husband had the courage to try something new. They began to make the change happen here, and now her having to walk miles away to collect firewood solved. The changed landscape, availability of firewood and pasture means her kids can go to school,” she said.
“Women can change the world. This was not an easy journey but the fruit of the work after they did this was so obvious that it became very hard for people to deny,” Clare told a group of local farmers who had come to see the success in Nancy’s farm model.