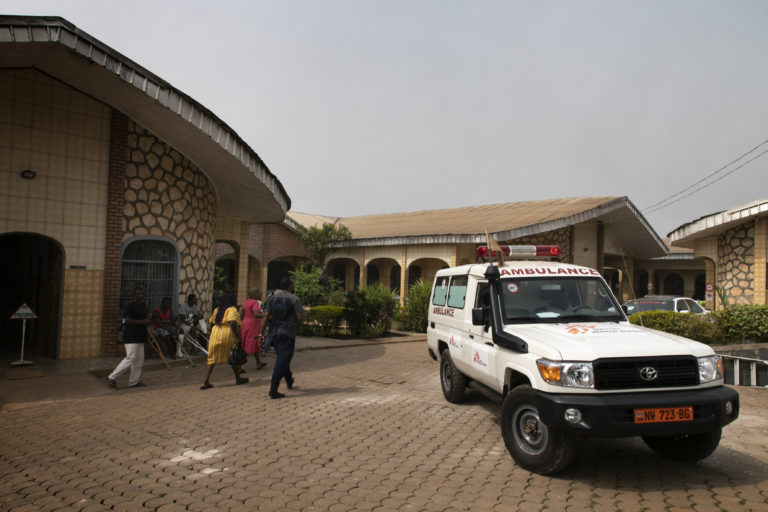
Tens of thousands of people are missing out on free essential healthcare services in the restive English-speaking North West Region of Cameroon as the government maintains a suspension on the activities of medical aid group Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Border (MSF) in the region.
Authorities had in December 2020 forcefully halted the work of MSF on claims that the charity was colluding with armed separatist fighters seeking to secede from Cameroon and create their own state named ‘Ambazonia’. MSF has repeatedly denied the accusation and says it stands by its charter which requires the provision of healthcare without discrimination or heed to political or religious affiliations.
Despite MSF’s denial of wrongdoing and the necessity of healthcare provision, the government has yet to lift the ban six months after. People continue to live in limbo in a region where the government itself recently acknowledged that 30 percent of health facilities were no longer functional due to the drawn-out conflict.
MSF has now called on the government of Cameroon to allow it to resume operations and provide much-need medical and humanitarian relief to people in distress. Authorities have officially not responded to the request.
According to Emmanuel Lampaert, MSF Operations Coordinator for Central Africa, it is unacceptable that people who have fled violence into blushes are denied vital medical services for six months and counting. “This decision represents a substantial blow to medical and humanitarian access.”
Since 2018 when Doctors Without Borders started its intervention in the conflict-plagued English-speaking regions of Cameroon, it has treated patients for rape, physical and psychological torture, burns and gunshots. MSF teams have also largely handled patients in need of medical assistance for childbirth, malaria or diarrhea. Last year alone, the charity attended to 150,000 people in troubled regions.
“As we speak, our community health workers see people die and suffer because of the lack of treatment available in villages and displaced communities, and our ambulance call center continues to receive emergency requests, which they are forced to decline. What rationale can justify these unnecessary deaths?” Lampaert bemoaned.
Recent recurrent battles between government troops and increasingly bold armed separatists have exacerbated insecurity. This, coupled with Monday ghost towns, curfews, occasional lockdowns and the targeting of health facilities, have gravely disrupted access to healthcare. Economic hardship brought about by the drawn-out conflict has made it difficult for people to be able to transport themselves to health facilities or even pay for treatment. Many hospitals have suffered arson attacks or have been repurposed into military bases.
Yenfui Delphine, a young mother based in Bamenda, told Ubuntu Times she is one of those who feel the pinch of the absence of MSF. While making allusion to her son who felt seriously sick two months ago, Yenfui said MSF teams used to be there for people who had emergencies but lacked a means of transportation and money. “Without them, it is very risky getting a sick one by motorcycle [the only option available] to the nearby health facility on a ghost town day,” she said.
In 2020, MSF teams in the North West Region treated 180 survivors of sexual violence; 1,725 mental health consultations were provided; 3,272 surgeries were performed; 4,407 patients were referred by ambulance, of which more than 1,000 were women in labor; 42,578 consultations were provided by community health volunteers, mostly for malaria, diarrhea and respiratory tract infections.
Lampaert said MSF staff, volunteers and patients have regularly faced threats and violence from both state and non-state armed groups, with very little respect shown for the humanitarian principles of impartiality and neutrality. “Our ambulances have been fired on and stolen, community health workers have faced sexual assault and murder, armed men have opened fire inside medical facilities, and our colleagues have faced death threats. Despite these extremely difficult situations, our staff kept on providing care to people in need, day after day.”
Since 2017, Cameroon’s two English-speaking regions have been ravaged by a bloody socio-political conflict. Low-level protests erupted in 2016 against decades of marginalization of the minority Anglophones by the Francophone-dominated government of long-serving President Paul Biya. The government responded with force and pushed many to the extreme, triggering an unending war.
To date, it is estimated that over 5,000 civilians, soldiers and separatist fighters have been killed, while no fewer than three million others are affected by the conflict. The war has internally displaced 712,800, according to OCHA and the UN refugee agency – United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) has registered 66,718 people who have crossed over the border to Nigeria as refugees.