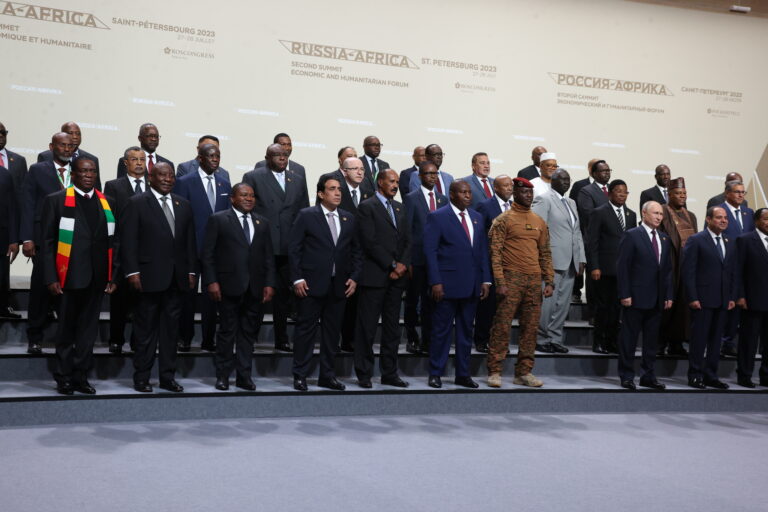
There are intense political and intellectual debates unfolding in Africa. Since February 24 last year, when war broke out in Europe following Russia’s special military operation in Ukraine, the presence of Russia in Africa has been politically extensive through mercenaries from the disbanded Wagner Group (WG) under the pretext of fighting neo-colonialism. Africans have questioned the developments even so, without getting a satisfactory consensus guided by a framework of the continent’s interests.
While abhorred, the occurrence of unconstitutional government changes through military putschs in Mali, Guinea, and Burkina Faso in the past two years and recently in Niger and Gabon has birthed a new fascination towards Russia among the young and old supporting the military leaders in their countries. Russia has embraced these military governments, mainly in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Niger, providing them with diplomatic backing and security assistance.
The backing of the military governments in Africa by Russia is changing the nature of relations between the two parties and has affected Africa’s relations with its former colonizers. To some, it is a partnership of unequals, a coalition with imbalances, and a patron-client relationship advancing the interests of the dominant party. To others, Africa is moving from one global giant to another to influence the operations of politics at a global level. This remains true with Africa’s relations with the United States, the European Union (EU), or China, where most outcomes are tilted in favor of partners other than Africa.

The advancements of Russian interests in Africa are not following the traditional carrot-and-stick policy of the West, but soft power enticements channeled through scientific and technological transfers, knowledge, and expert skills to be acquired through Russian language at schools to be set in Africa. This was agreed at the Russia-Africa Summit held from July 27 to 28 this year in St. Petersburg, Russia. Some African leaders who agreed to this were charismatic Burkina Faso’s Ibrahim Traore, Eritrea’s Isaias Afwerki, South Africa’s Cyril Ramaphosa, and Zimbabwe’s Emmerson Mnangagwa, among others. This was confirmed by the current African Union’s (AU) chairperson, President Azali Assoumani of the Union of Comoros.
Director of Research, Africa Center for Strategic Studies at the University of Maryland, Dr. Joseph Siegle, has noted that “none of Russia’s objectives are about making Africa more prosperous or stable. Rather, the continent is primarily a theater to advance Russia’s geostrategic interests.”
In light of this, public intellectuals and academics remain divided.
Coloniality and Colonization 3.0
The agreement on a cooperation action plan by Russia and Africa for the establishment of institutions in Africa that will use Russian as a medium of instruction has been interpreted as an attempt to colonize the being of Africans, take away their power, and replace their knowledge.
International relations analyst and principal researcher at the Zimbabwe Democracy Institute (ZDI), Mr. Bekezela Gumbo, says Africa needs to assess Russia’s actions and measure them on the yardsticks of “being, power, and knowledge.”

Mr. Gumbo sees Russia as a country keen on enjoying what Africa’s former colonizers enjoyed, but without using brute force.
“When you look at educational institutions, you see that the coloniality of knowledge comes from education systems. When the Russian language is used as a medium of instruction, it means Russian ethics and standards of education will be used.
“This will reproduce Africans that are better placed to serve Russia’s interests. The Russia-Africa Summit was not neo-colonization but was colonization 3.0, where instead of using brutal force, anticipated force is used to effect colonization 3.0, where Russia is now in charge as a new colonizer who uses covert and not brutal force,” says Mr. Gumbo.
The situation presents Africa as a desperate player who needs Russia to protect her from the former colonial system.

Mr. Gumbo added that “this is not different from what happened during the colonial era. It is either you join Russia or you face the wrath of your former master or colonizer. The impression being built is that without Russian support, you might not be safe, despite being an all-weather friend. They may sponsor a coup and work with the young generation fascinated by pro-Russian ideology.
“Essential pillars of coloniality are in what Russia wants in Africa, that is power. Russia is now wanting to get to power by accessing the mind and being of the African man.”
Assessments by Mr. Gumbo have been reinforced by Dr. Felistas Zimano, who is convinced that what Russia is doing in Africa equates to “100 percent neo-colonialism.”
“This is 100 percent neo-colonialism. The interest that Russia has in pushing its language to Africa is the issue that should make Africa mostly worried. This defeats any stride towards the unification of Africa.
“A people’s glue is in its culture; a people’s culture is retained in its language. Once that is eroded, then there will not be any Africa to talk about. If anything, this reinforces the notion that all they see of Africa are mere pawns,” she said.
Missing the Point
Senior politics and international studies lecturer at the University of Zimbabwe (UZ), Dr. Prolific Mataruse, believes there is a protracted effort to smear Russia as having imperial designs in Africa. He emphasizes that by engaging with Russia and other countries like China and learning their languages, Africa is subverting the colonial businesses and thought.
Dr. Mataruse concluded by adding that “in all fairness, talking about Russia having imperial designs is missing the point. The whole point of African relationships with Russia, China, Turkey, India, and other countries and learning their languages is an issue of promoting a multiverse approach away from the monoverse dominance of Anglicized language. Learning other languages besides English is subverting colonial systems of business and thought.”