Across the African continent, an unprecedented wave of youth-led uprisings is shaking the pillars of political regimes that have held power for decades. In Kenya, Uganda, Mali, Burkina Faso, and beyond, young people are rising against systemic corruption, unemployment, and political exclusion.
The youth—armed with mobile phones, social media platforms, and a hunger for change—are rejecting the status quo, demanding accountability, justice, and an active role in shaping the future of their nations.
In Kenya, a vibrant and youthful nation where nearly 75 percent of the population is under 35, young people have found their voices louder than ever. They flooded the streets, their chants echoing across Nairobi’s sprawling skyline, through the dusty roads of Kisumu, and along the coastal corridors of Mombasa. Armed with placards and burning passion, they marched against the suffocating economic reality and political ineptitude that have stalled their future.
This year’s protests are not the first, but they are perhaps the most poignant. Large-scale demonstrations have gripped the nation, pushing thousands of youth into the streets in a spontaneous combustion of frustration. At the heart of their anger lies a cascade of grievances—soaring unemployment, rising cost of living, and the government’s unfulfilled promises. The protests are a physical manifestation of the pent-up disillusionment many young Kenyans have carried for years.
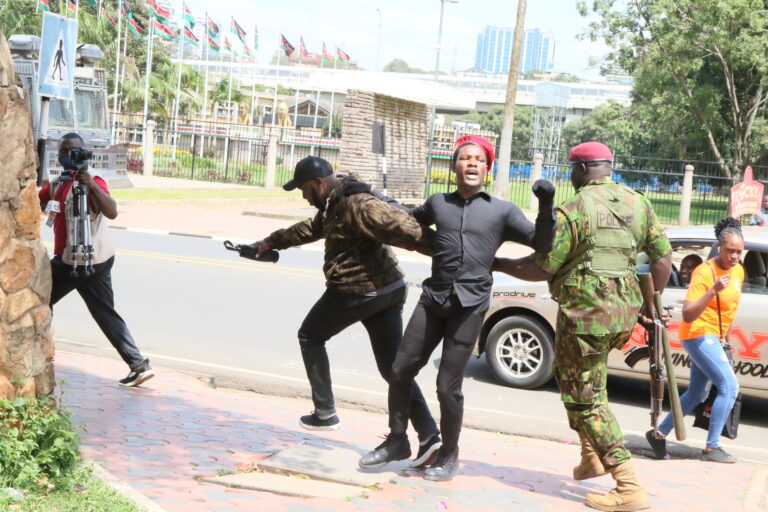
In one such demonstration, the air was thick with the smell of burning tires and the acrid sting of tear gas. As riot police formed imposing lines, their shields gleaming in the harsh sunlight, protestors responded with chants demanding justice. They carried banners that read, “Reject Finance Bill,” as they called for the complete resignation of political leaders they see as corrupt and indifferent to their plight.
Among them is 23-year-old Agnes Wanjiru, a bright-eyed student leader at the University of Nairobi. “We are tired of being ignored,” she says, her voice rising above the crowd. “We are told to be patient, but for how long? We have degrees, but there are no jobs. We cannot keep waiting for things to change—we have to make the change ourselves.” Agnes, like so many of her peers, sees the protests as a final stand, a last opportunity to salvage a future that seems to be slipping through their fingers.

The response from the government has been swift and brutal. In an attempt to quell the unrest, security forces were deployed to various hot spots, using tear gas, rubber bullets, and mass arrests to suppress the protests. But the heavy-handed tactics only served to inflame the movement, emboldening the youth to continue fighting for a democracy they feel is slipping away.
Kenya’s youth have grown up in a country where economic opportunities remain scarce. Despite being better educated than any previous generation, they find themselves locked out of the very system that promised prosperity. Corruption, which syphons off billions meant for infrastructure, healthcare, and education, has eroded their faith in government institutions. It is a betrayal that cuts deep.
“We watch as politicians drive around in luxury cars, build mansions, and send their children to study abroad, while we can’t even afford a meal,” says Brian Kamau, a 27-year-old recent graduate who has yet to find a job. “This is not the Kenya we deserve. We want leaders who care about the people, not their own pockets.”
The anger has been brewing for years. Once leaders take office, they quickly forget the political promises made to the youth during elections. Leaders promise jobs, economic reforms, and opportunities to young people during elections, but these promises fade into oblivion once the votes tally. This cycle of broken promises has left many feeling disenfranchised and voiceless.
“We’ve waited long enough,” Kamau continues. “The government has failed us. If we don’t fight for our future now, then we will be condemned to live in this misery forever.”
A Growing Movement: Lessons from Uganda and Beyond
Kenya’s youth-led movement is not happening in isolation. It is part of a broader continental pattern where young people are rising against authoritarianism and ineptitude. Just across the border in Uganda, a similar story is unfolding.
In a seemingly innocuous act, Edward Aweba, a young Ugandan activist who poked fun at Uganda’s long-standing president, Yoweri Museveni, on social media, was recently arrested. This incident serves as another example of the government’s ongoing crackdown on youth dissent.
His arrest, like that of many other young voices in the country, has sparked widespread outrage, especially among Uganda’s youth, who are increasingly becoming vocal against President Yoweri Museveni’s long-standing regime.
While details surrounding Aweba’s arrest remain scarce, early reports suggest he was detained for his outspoken criticism of the government, potentially linked to his involvement in organizing or participating in protests. The youth in Uganda, emboldened by rising frustrations over economic hardships, limited freedoms, and a lack of political representation, have become a formidable force against the authoritarian grip of Museveni’s administration.
This arrest adds to a growing list of young Ugandans facing state repression for challenging the status quo, fueling the #FreeAweba movement online. The youth are increasingly using social media to spotlight injustices and build solidarity across borders. In a nation where freedom of speech is constantly under siege, the arrest of activists like Edward Aweba reflects the regime’s fear of the power the youth wield.
Uganda, like many other African nations, is witnessing a generational struggle between entrenched leaders and a younger population yearning for change, dignity, and a brighter future.
Like their Kenyan counterparts, Uganda’s youth are calling for more than just political change. They want dignity. They are rejecting the idea that they must quietly endure the hardships inflicted upon them by a government that seems more interested in maintaining power than improving lives.
From Mali to Burkina Faso: The Military Solution
While Kenya and Uganda’s youth are rising in the streets, West Africa is witnessing a different kind of uprising. In Mali and Burkina Faso, frustrations with civilian governments that failed to address security challenges or curb corruption have led to military coups, driven by young soldiers and their supporters.
In Mali, the military ousted President Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta in 2020, with many young Malians cheering on the takeover. They believed the military would bring stability where civilian leadership had failed. A similar situation unfolded in Burkina Faso, where young soldiers overthrew President Roch Marc Christian Kaboré.
Yet, even as these coups raise hope for some, they also ignite fear. “We wanted change, but now we’re not sure what kind of change we will get,” says Fatoumata, a 26-year-old activist in Ouagadougou. “We don’t want military rule to become the norm. Democracy is what we fought for.”
A Pan-African Call for a New Future
The youth-led uprisings across Africa—whether in Kenya, Uganda, or West Africa—are part of a larger movement. With over 60 percent of the continent’s population under 25, young people are now the most significant force of change. They are no longer waiting for power to be handed to them. They are taking it.
From Nairobi to Bamako, the demands are the same: economic justice, political representation, and an end to corruption. But perhaps most importantly, these movements are about reclaiming dignity. Young Africans are rejecting the paternalistic systems that treat them as passive subjects rather than active citizens.
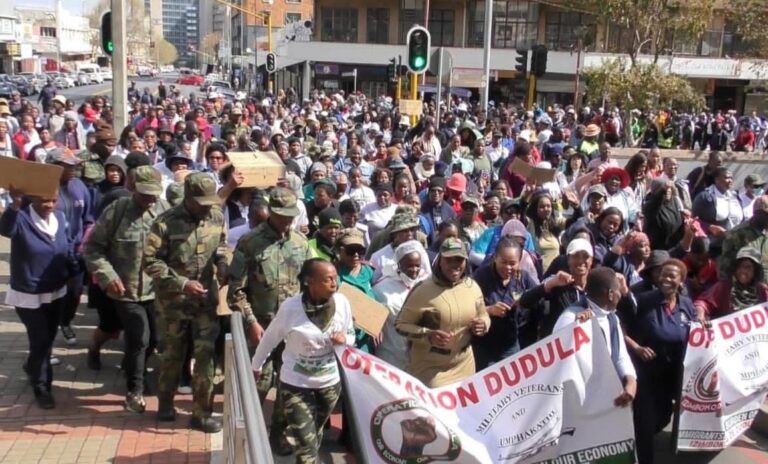
They are building solidarity across borders, using social media to connect and share tactics. The #EndSARS protests in Nigeria, which aimed to dismantle a corrupt police unit, inspired youth movements across the continent. Similarly, the student-led #FeesMustFall protests in South Africa have served as a rallying cry for those demanding educational reforms elsewhere.
The youth uprisings in Kenya and across Africa mark a critical turning point in the continent’s history. Governments, long accustomed to ruling without accountability, are now facing an unstoppable force. Whether through protests, social media campaigns, or outright revolutions, young Africans are declaring that their time is now.
The path forward is uncertain, but one thing is clear: Africa’s youth will no longer be silenced. They are reshaping their countries, their governments, and the future of the continent. And as they march forward, fists raised and voices booming, they are reminding the world that Africa’s greatest asset is not its minerals or its land—but its youth.