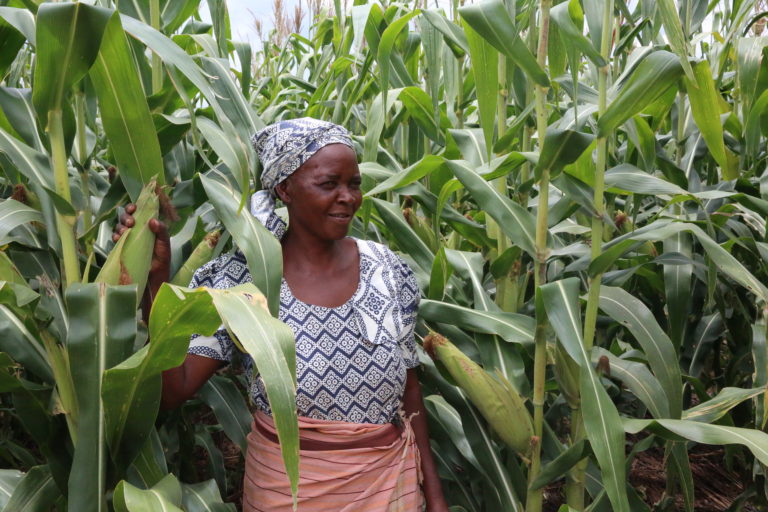
Marange, Zimbabwe — It is a windy day in Marange, Chanakira village. Small clouds scuddle the blue sky giving it a blurred look. About 110 kilometers southwest of Mutare, Norah Mwastuku (48) a subsistence farmer sits at the verandah and contemplates when the first rains will arrive.
She anxiously looks at her fields, decorated with mulched holes.
Mwastuku is one of the farmers who have embraced the Pfumvudza program — a concept where crops are planted on zero tillage in a bid to conserve water and inputs on a small piece of land.
She is enthusiastic about the program and is looking forward to the new season.
“I have already dug holes in a 39 meters by 16 meters piece of land. This coming season I am planning to grow maize,” the mother of four told Ubuntu Times.
This area does not receive much rain and farmers like Mwastuku rely on boreholes to water their fields. The soils are tired too.
While the government is currently popularizing the Pfumvudza program, Mwastuku is used to it. In the season 2019/2020, she grew maize and sorghum at the same size of land as part of Pfumvudza.
“I had a good harvest. This is what we are surviving on as a family,” she said. The farming concept is increasingly becoming popular among farmers in areas that receive less rainfall.
Lilian Murangariri (50), a small-holder farmer from Headlands, about 140 kilometers from the capital Harare says Pfumvudza has less labor.
“Last year I grew orange maize and white maize in a half-hectare piece of land. I was amazed with the harvest. As a farmer you do not have to stress about using cows for tillage as this is zero tillage,” she told Ubuntu Times.
The mother of three says Pfumvudza is economic and can be practiced by farmers who do not have enough farming machinery.
“The holes and mulch conserve water. I can still harvest my crops even if there is poor rain. I also use less inputs such as fertilizer,” said Murangariri.
Mwastuku and Murangariri are some of the over 9,000 people who have embraced Pfumvudza with the support from the Zimbabwe Livelihoods and Food Security Programme (LFSP).

The LFSP, which is funded by the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office (FCDO), is managed by United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and implemented by Welthungerhilfe, Practical Action and World Vision.
It is aimed at reducing poverty, targeting 250,000 rural farming households through improved food and nutrition security and incomes in 10 districts in Zimbabwe.
LFSP trained over 50,000 farmers from their clusters in Manicaland, Midlands, and Mashonaland Provinces in 2019.
For the past half a decade Zimbabwe has been having incessant droughts and floods which, according to experts, are caused by climate change.
Nearly 8 million people, about half of Zimbabwe’s population, are food insecure, according to the United Nations’ World Food Programme.
The southern African nation, which was once the breadbasket of the continent, will import an estimated 1.1 million tonnes of grain in the 2020/2021 marketing year to meet demand, according to the FAO.
This Pfumvudza concept which was spearheaded by FAO last season in Zimbabwe has been adopted by the President Emmerson Mnangagwa led government in the 2020/2021 season targeting nearly 2 million households, about 10 million people.
The government is supporting these farmers with inputs.
Prudence Mucharwa, a small-holder farmer in Chihota near Marondera, about 70 kilometers from the capital Harare, said she is new to the concept.
“I joined Pfumvudza a bit late. I met an Agritex officer who explained it to me. The Grain Marketing Board will loan me inputs and I will pay back with maize or soya meal,” she said.

Lands ministry permanent secretary John Bhasera explains more about the program.
“Pfumvudza is simply conservation agriculture. This is basically conservation which has been nationalized. It has minimum soil disturbance as well as mulching creating a blanket of cover so that you can conserve moisture. Crop rotation as well, we have three farming sectors—one for [a certain type of] cereal, another for [a different] cereal and the last for other crops,” he said.
Zimbabwe has been having farming schemes for the past decades but still, farmers are producing grain not enough to feed the nation.
There is a need for new tactics.
“We now have a new extension approach which is called Train, Track and Monitor (TTM). We have sourced motorcycles for our agriculture extension workers across the country so that they are able to practice the TTM approach. We started with training. We trained the Agritex officers for nearly a month. Now the extension officers are training farmers,” Bhasera said

Olga Nhari, Women in Agriculture Union chairperson speaks glowingly about the program.
“Of the three plots one produces yield sufficient for family and the other two plots for national storage,” she said.
Nhari said Pfumvudza helps rural women, especially, to fight against hunger and to improve livelihoods.
Zimbabwe Farmers Union executive director Paul Zakariya said there was a need to reverse the current state of affairs, where Zimbabwe has remained a net importer of staple cereals.
“It is not desirable that a country that has excellent agricultural lands and enjoys excellent climatic conditions, should import all its food,” he said.
In the past, farming schemes have been marred by corruption in the distribution of inputs as well as loan allocations. Some experts fear that the culture might continue under the Pfumvudza program.
“To say it is an opportunity to loot funds needs intelligence on whether the program will have a budget allocation and the actual implementation of the project in terms of funds or inputs allocation,” Harare based economist Victor Bhoroma told Ubuntu Times.
“However, almost all the country’s agricultural subsidy programs have flopped because of politicization of inputs distribution, corruption, inefficient funding or repayment models and lack of private capital participation which is tied to complicated land tenure policies,”
He said most of these agriculture programs are more political than economic of which in politics, the end justifies the means, hence, the government can pursue an economically costly program because it serves political interests.

Another economist Vince Musewe said Zimbabwe has invested in previous farming schemes but the country still imports grain.
“We have invested billions (of dollars) in Command Agriculture and we still have to import. We, however, need a new mindset that farming is a business and not a hobby where farmers expect to get free inputs,” said Musewe adding that a strong private sector drive in agriculture is important.
Zakariya said there is a need to put in place measures to curb abuse of inputs under such schemes.
“Without effective and efficient systems, the world over, abuse can be rampant,” he said.
From Pfumvudza, the government is expecting about 1.8 million tonnes of grain, which is almost 90 percent of the national food requirements.
During the 2020/21 season, the LFSP aims to incorporate agroecology aspects as subsistence farmers like Mwastuku realize the fruits of their sweat.
It is hoped that agroecology will better climate-proof smallholder agriculture production and will ensure nutrition for 50,000 households.