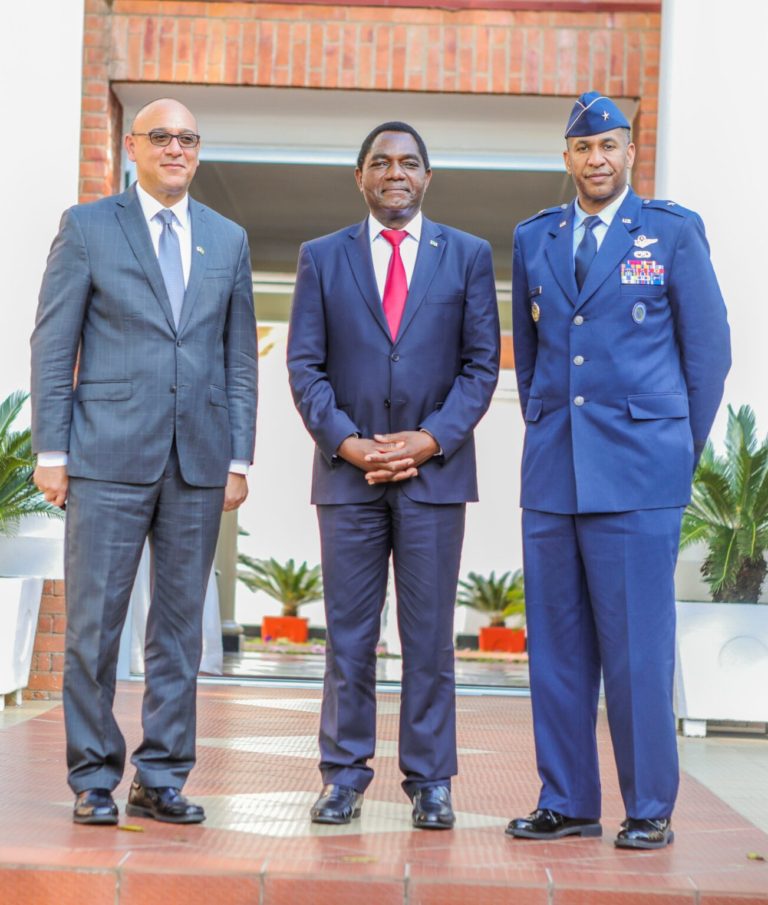
The United States of America’s military footprint has been felt in Southern Africa after a security pact signed between Zambia’s President Hakainde Hichilema and the US embassy in Lusaka on April 25 received both condemnation and commendation across the regional political divide.
There are fears the presence of US forces through the Africa Command’s Office of Strategic Cooperation in Zambia will create new insecurities for the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region than those that existed before, both traditional and non-traditional threats.
When AFRICOM was formed in 2007, two African countries, Botswana and Liberia, considered hosting it before Thabo Mbeki, then South Africa’s president and his Defence Minister Mosiuoa Lekota opposed the idea.
“That would constitute an unacceptable violation of Africa’s sovereignty,” Mbeki said then.
On August 29, 2007, SADC announced its position “that it is better if the United States were involved with Africa from a distance rather than be present on the continent.” Then SADC Defence and Security Ministers further stated “that sister countries of the region should not agree to host AFRICOM and in particular, armed forces since this would have a negative effect. That recommendation was presented to the Heads of State and this is a SADC position.”
Then Zambia’s president Levy Mwanawasa reaffirmed Zambia’s stance on October 2, 2007, when he stated “none of us is interested” in hosting AFRICOM forces.
The move by Hichilema, nine months after winning the presidency in 2021, is the first by a SADC member state to go against the bloc’s strategic culture.
“We are pleased to announce that US Africa Command will open an Office of Security Cooperation at the U.S. Embassy in Zambia. Visiting AFRICOM Brigadier General Peter Bailey made the announcement during a meeting with His Excellency President Hichilema,” read the tweet on the embassy’s official handle.
The US military footprint in the horn of Africa and its central command’s military operations in the Middle East, Asia and South East Asia and North Africa have exacerbated, not ameliorated insecurity and instability.
Disclose Contents Of Cooperation Agreement
Political leaders have called on Hichilema, who campaigned on a ticket of transparency and accountability, to publicise the contents of the cooperation agreement entered into between his country and the US.

Acting secretary-general of the former governing Patriotic Front (PF) party, Nickson Chilangwa, in a statement on May 1 demanded “that President Hichilema and his Government make full disclosure of the content and nature of the agreement he has made with the Americans.”
Chilangwa said president Hichilema acted unilaterally without constitutional authority, consultation and consensus from the citizens.
“Why were the Zambian people not consulted before such a monumental decision with far-reaching consequences was made? America is at war with several nations and allowing them to set up a military base here in Zambia directly puts Zambia in harm’s way with all those fighting with America.
“We demand that the President rescinds his decision to allow America to set up a military base or a military command centre on our soil.
“Allowing a foreign power to establish a military base on our soil does not only put us in grave danger of deadly repercussions from those opposing America but deeply compromise our own national security and leaves us bare to attacks and manipulations by others,” said Chilangwa.
Chilangwa said the speed with which President Hichilema and his United Party for National Development (UPND) government are “turning Zambia into a colony or appendage of the West is a great source of concern to all well-meaning Zambians.”
The PF’s position and reprimand on president Hichilema have also been buttressed by Zambia’s Socialist Party. A statement by the Socialist Party rejected the establishment of the Office of Security Cooperation with AFRICOM citing five reasons.
“There is a real danger of the country’s military doctrine being hijacked through this form of security cooperation. It will be extremely dangerous and fatal to turn the Zambia military into some extended arm of the American military.
“The US military operates not only to provide an advantage to the United States and its ruling elites, but it functions, along with the armies of the other NATO nations, including France, as the guarantor of Western corporate interests and the principles of capitalism,” read the Socialist Party statement.
Firefighting! No Smoke Without Fire
Both the President and Zambia’s ministry of defence have come out dismissing claims that there are no AFRICOM bases soon to be set up in the southern African country.

“There are only Zambian military bases in Zambia. Let’s not be debating falsehoods,” tweeted president Hichilema two days after his defence minister Ambrose Lufuma played down the talk of AFRICOM military bases in Zambia.
Said minister Lufuma: “The AFRICOM being referred to on social media platforms is based in Germany and the Zambian government has not at any given time agreed to move to Zambia.”
Lufuma also warned those fanning misinformation.
“The ministry of defence would like to take this opportunity to warn all perpetrators of such misinformation meant to tarnish our existing cordial relationship with our neighbours and strategic partners to desist from issuing alarming statements which hinge on the security and territorial integrity of our nation,” he warned.
Who Can Turn Down US friendship?
Zambia’s governance expert McDonald Chipenzi argues that the position taken by Zambia is within her national interest in the face of an ever-growing threat from Islamist militants in neighbouring Mozambique. He says no country would turn a blind eye to partnering with the “mighty US.”
“The hard fact is that there are very few countries in the world that would not like to partner with the mighty US in broad daylight or in the night (daylight or behind the closed doors).
“Let us not only look at security from the physical aspect, but also logically too and we have to ask ourselves a few questions such as who controls the space? Who controls our technological portals, our cyber highways? Who controls the Electronic City?
“We use the Windows on our computers as our operating systems in our offices or even in Vulnerable Points (VP), our would-be High Valued Targets (HVT) but who has the back door details of these gadgets if it is not America?” asked Chipenzi.
Chipenzi added Zambia’s interests are a priority in an ever-changing global environment.
Security Headache For SADC
University of Zimbabwe International Security and Strategic Studies lecturer Dr. Lawrence Mhandara said the presence of the AFRICOM in SADC is the continuation of the US pursuit of influence in the midst of competition from other global powers through other means.
“The competition is expanding in spatial terms. International influence can be achieved through economic, diplomatic, military and informational means. In this case, the US is making a rational decision to use its military capabilities to impose itself on Southern Africa, in particular extending its approach of international basing, and security cooperation.
“The bilateral arrangement validates the long tradition of US statecraft whose cornerstone is a militarized foreign policy. History has ineffaceable evidence showing a proclivity by the superpower to implement foreign policy through coercive instruments in a sequenced fashion,” said Dr. Mhandara.
The anticipated presence of the AFRICOM in Zambia leaves regional leaders with more to think about, given the affluent history of American interventionism and its colourful brand of intrusive politics.
In this regard, the militarization of US foreign policy is seen as the substratum of its status as a superpower yet an agonizing and tragic reality with the potential to supply complicated security risks and instability in Southern Africa.
SADC, indeed Africa, is likely to be afflicted by a host of security challenges as great power competition for influence and control intensifies. The move by America is likely to elicit responses in kind from other global powers keen on counteracting the undesired influence.
The US is furthermore attempting to regain influence in a region dominated by Chinese allies. But the choice of the military instruments to mediate this competition may have cataclysmic outcomes.