The Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) might have been defeated, but its ideas and followers did not disappear. It has since reappeared in Mozambique’s northern Cabo Delgado Province, transformed as the Islamic State’s Central African Province (ISCAP). In August last year, the group attacked and ran over Mocimboa da Praia, a port town lying on the Indian Ocean coast, declaring it its capital and raising the ISCAP profile to the world.
The situation at present is threatening a major military and humanitarian crisis, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) which has so far internally displaced at least 700,000 people. By June, the number is projected to be around one million.
Raouf Mazou, UNHCR’s assistant commission for operations recently said: “If one looks at the speed at which we are seeing the number of internally displaced persons rise, we know that the window of opportunity that we have is closing.”

The roots of the insurgency in Mozambique on October 5, 2017 can be traced to Kenya’s city of Mombasa and spreading along the coast in Tanzania to Mozambique. Where a combination of resources and conflict pan, the United States has presented itself as a counterterrorism partner. Over 2,000 US forces are active in over 40 counter-terrorism training missions in Africa.
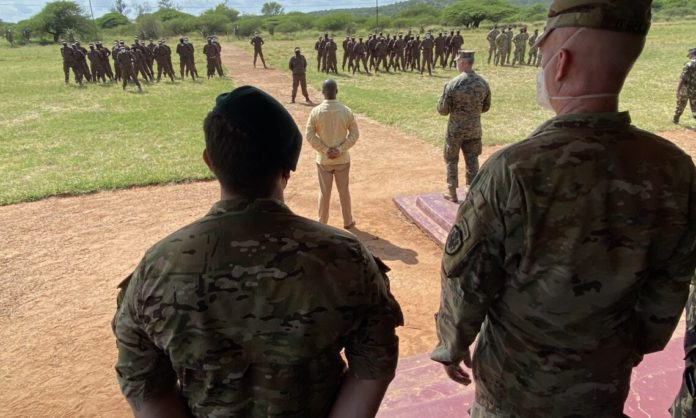
Mozambique, a member of the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC), on March 15 confirmed the presence of US Commandos in the country for the next two months. A statement by the US embassy in Mozambique revealed that the arrangement is a government to government arrangement in which “US Special Forces will train Mozambican marines for two months to support Mozambique’s efforts to prevent the spread of terrorism and violent extremism.”
This marks the entry of the US-Africa Command in a region that has enjoyed relative peace. On the other hand, Mozambique’s former colonizer, Portugal, confirmed it will send “a staff of approximately 60 instructors to Mozambique to train marines and commandos.”
Is Mozambique Choosing A Wrong Ally?
The SADC bloc has a counter-terrorism strategy that underscores the desire to mete out terrorism and violent extremism under the collective belief that “a threat to one country threatens the peace and stability” of other countries.
University of Zimbabwe (UZ) lecturer in the Department of Politics and Administrative Studies Dr. Lawrence Mhandara says the decision by the Mozambican government to invite US forces “indicate a vote of no confidence” on the regional bloc.
“The lack of action on the Mozambique issue by SADC demonstrates a lack of collective capacity in the region. Though SADC has a counter-terrorism strategy, it lacks dynamism in dealing with collective security threats. For instance, Angola and Zimbabwe lack counter-terrorism capabilities,” notes Dr. Mhandara.
The SADC protocol to assistance from other nations is based on the “invitation by the country that needs help” so that other countries intervene. In the case of Mozambique, the country only sent an invite in August last year after it had approached individual countries, which did not yield results. The choice of the US by the Mozambican government, according to Dr. Mhandara, “could be based on the USA’s combat experience” on several conflicts fighting terrorism.
US forces have notably been to Afghanistan, Iraq, Somalia and now in Syria in the name of “fighting” terrorism.
“The obvious implication of this action by the government of Mozambique is that it envinces a vote of no confidence in the collective will and capability in SADC. There could be some incentives for the USA in this arrangement, but it is damaging to SADC,” added Dr. Mhandara.
Resource Protection At The Heart Of Foreign Intervention
The involvement of the US in Mozambique is part and parcel of the political-economy of war. It cannot be refuted that there are incentives for the US in this conflict. In Afghanistan and Iraq, American companies have benefitted from defense contracts through conflicts.
There are double standards coming through over the past ten years, oil companies have discovered the largest gas reserves that push several multi-billion dollar projects that have the potential to turn Mozambique into the next energy giant. As of 2019, statistics indicate Mozambique holds 100 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of proven gas reserves, and ranked 14th in the world. In 2011, economic projections from the World Bank pointed that in the next ten years, the biggest investments were going to Cabo Delgado.
In the Cabo Delgado region, Montepuez ruby mine is said to account for 80 percent of global gas output. Besides Montepuez, a myriad of private gas companies have also emerged and protecting their interests by hiring private security companies to protect their interests. When ISCAP ran over Mocimboa da Praia last year, the Mozambican government and French oil company Total announced a strengthened agreement to protect gas installations including the Rovuma LNG gas project led by Italy’s Eni and the USA’s ExxonMobil.
The US and Portuguese troops coming to Mozambique are members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) keen to “stop terrorism and extremism.” Simultaneously, they are protecting the economic interests of French’s Total, Italy’s Eni, and USA’s ExxonMobil, exploring gas in Mozambique. France and Italy are also NATO members.
“After this conflict, aims could be economic for the US government and after the mission, certain benefits will accrue to the USA,” further notes Dr. Mhandara.
Mozambique’s President Fillipe Nyusi has also been accused by his critics of pushing the neo-liberal agenda that prioritizes business over ideological principles as enunciated in the SADC framework to solving conflict, ending poverty and ensuring economic development. According to the World Bank, half of rural people in Mozambique live below the poverty line, a figure barely reduced since 2003.
ISCAP Using Religion To Tap Into An Illegal, Neglected Economy
Cabo Delgado has corridors that can improve trade between Tanzania and Mozambique, and the province is said to have an illegal economy used for heroin smuggling from Asia worth an estimated US$100 million which ISCAP is tapping into.

The conflict in Cabo Delgado also has a religious twist. The region is one of the country’s poorest and mostly resident to Muslims. It has the lowest literacy rate, too. The Muslims in Cabo Delgado have over the years felt neglected as the natural gas in their province has not generated any benefits in their communities. ISCAP is using this to promote its anti-State agenda.
US Unwanted Yet Welcome In SADC Region
SADC Executive Secretary Dr. Stergomena Lawrence Tax is of the view that the region is “collectively committed” to supporting its member States, including Mozambique, in dealing with matters of insecurity that threaten the stability of the region at large. She confirmed the region has a robust policy, institutional and implementation framework to deal with issue of insecurity, including violent extremism and terrorism in Mozambique, without explaining why Mozambique invited the USA and by-passing SADC.
“Terrorism is a global challenge, as such, solutions to the insurgency require collaborative efforts among member states, regional communities and international partners. SADC has taken a multi-sectoral approach in ensuring that such challenges are addressed comprehensively and sustainably at national and regional levels. This is done through a number of policies, strategies and programs,” she said.

There are some issues the SADC region is not addressing, the spill-over of the conflict to Mozambique’s neighbouring countries. Because of the spatial proximity, conflict and threats of terrorism are likely to be huge in Malawi and Tanzania as neighboring countries.
SADC has long and winding borders that are not policed and monitored, hence for a long time have been porous and conducive to move contraband. The threat of refugees moving from Cabo Delgado into Tanzania and Malawi is great and this can be an opportunity by the ISCAP to export the terror operatives in other countries embedded as refugees.
Regarding possible outcomes to the conflict, Dr. Mhandara argues there is a possible spill-over of the conflict that is set to welcome US military presence in SADC.
“Because of the conflict going on in Cabo Delgado, the immediate issue is that the military presence of the USA will be immediately welcome though unwanted. The USA will then influence and capture the region through counter-terrorism and counter-insurgence experience and in the long term there will be presence of the USA in the region,” added Dr. Mhandara.
According to SADC, there is provision of a Standby Force for the Mozambique conflict if member states pledge support. This has however not happened except for the “collective solidarity” rhetoric by the regional leaders. The response by the region remains a feeble and futile adventure that should be quickly addressed to ensure regional stability.